Silver, often referred to as the “poor man’s gold,” has captivated traders and investors for centuries due to its unique characteristics and historical significance. Recently, it has gained attention as an alternative investment, aligning with the growing interest in precious metals amid economic uncertainties and inflation concerns, highlighting its potential as a viable trading option. The current estimated market cap of silver stands at approximately $1.3 trillion.

Traders utilise silver for diverse purposes such as investment, speculation, and hedging against economic volatility. It acts as a potential store of value and a hedge against inflation, appealing to those diversifying portfolios or managing risk during uncertain economic times.
In this guide, we will delve into the world of silver trading, offering valuable insights and essential knowledge for those embarking on their silver trading journey.
Silver, often referred to as the “white metal,” boasts a rich historical legacy dating back thousands of years. Its journey from ancient civilisations to the modern world is deeply entwined with human society and economic development.
Silver has been a prized commodity since ancient times. In Mesopotamia around 2500 BC, the first known silver mines were established, signifying the early recognition of silver’s value. It was used for various purposes, including as jewellery, utensils, and as a form of currency.
Silver’s role as a medium of exchange evolved across civilisations. The Greeks, Romans, and other ancient civilisations used silver in their coinage systems. The Roman denarius, for instance, was a widely recognised silver coin. In medieval Europe, the ‘Troy pound’ of silver emerged as a standard measurement, emphasising its importance in trade and commerce.

During the 19th and early 20th centuries, many nations adopted the silver standard, tying their currency values to a specific amount of silver. The United States, for example, had a bimetallic standard where both gold and silver were used to back the value of the dollar. However, due to economic challenges, many countries later shifted to the gold standard.
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th century brought about a transformation in silver’s significance. Its exceptional electrical conductivity and other physical properties made it crucial for various applications. Silver became an essential component in photography, electronics, batteries, and more. This transition from primarily being a monetary asset to an indispensable industrial metal significantly impacted its demand and market dynamics.
In contemporary times, silver’s historical significance continues to influence its trading appeal. Traders and investors appreciate silver not only for its industrial applications but also for its enduring value as a precious metal. This dual nature positions silver as a unique and versatile asset in the modern financial landscape.
Silver, a unique commodity, combines both precious and industrial metal qualities. This dual identity drives diverse demand and holds a crucial role in various industries.

Historically treasured for its rarity and aesthetic appeal, silver’s shiny appearance and scarcity make it a preferred material for crafting jewellery, ornaments, and prized artifacts. In industry, its exceptional conductivity is indispensable for electronics, solar panels, medical devices, and chemical production. Additionally, silver’s reflective properties make it a fundamental component in specialised mirrors.
Several factors influence the prices of silver, making it essential for traders and investors to stay informed and analyse these aspects for effective decision-making in the silver market.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The interplay between the supply and demand for silver is a fundamental determinant of its price. Factors such as mining production, recycling rates, industrial demand, and investor interest all impact the overall supply and demand equilibrium.
Geopolitical Events
Silver prices can be significantly influenced by geopolitical events, including political instability, wars, trade tensions, and policy changes. These events can create uncertainty in the market, affecting both demand and supply.
Economic Indicators
Key economic indicators like GDP growth, employment rates, inflation, and monetary policies directly affect silver prices. Silver often experiences increased demand during times of economic growth and stability.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a vital role in shaping silver’s demand. Emerging technologies that rely on silver, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions, can substantially impact its price.
The gold-silver ratio is a fundamental metric in silver trading, indicating the amount of silver needed to purchase one ounce of gold. This ratio is a valuable tool for traders, offering insights into market sentiment and potential overbought or oversold conditions in the silver market.
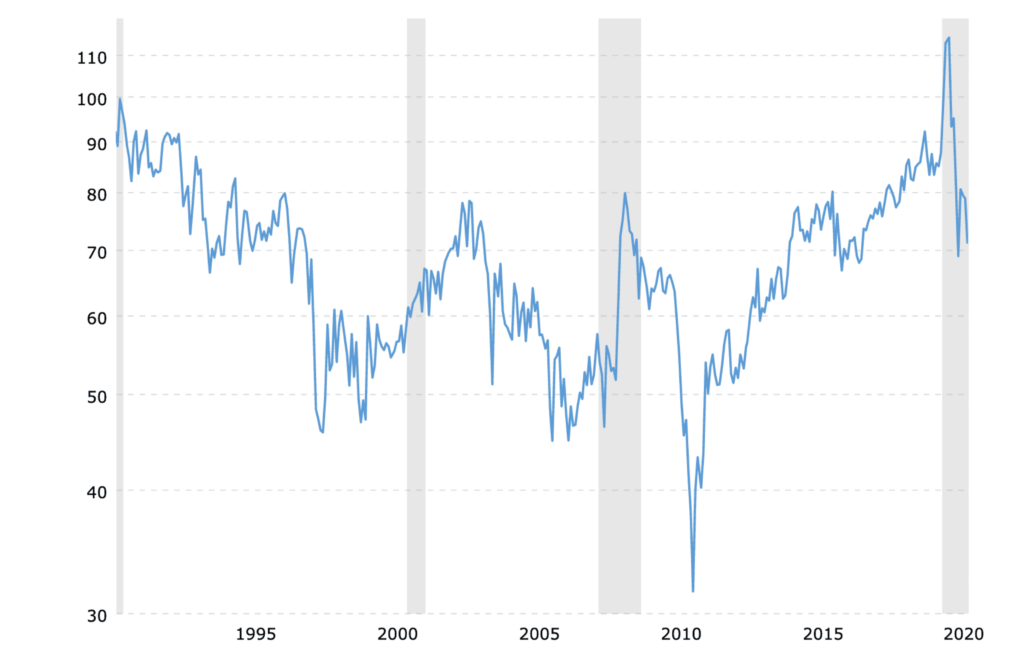
A higher ratio implies that silver is undervalued compared to gold, suggesting it might be an opportune time to buy silver or sell gold. Conversely, a lower ratio suggests silver is overvalued compared to gold, potentially signalling an opportunity to sell silver or buy gold.
Traders utilise this ratio to strategise their investments, deciding whether to focus on gold or silver based on market conditions. Additionally, shifts in the gold-silver ratio can reflect broader economic trends and investor sentiment, offering valuable insights for traders navigating the silver market.
Understanding the correlation between silver and other markets is crucial for predicting price movements and making informed trading decisions in the silver market.
Silver has significant correlations with various markets, including:

Various avenues exist for trading silver, each offering unique opportunities and considerations. Understanding the diverse forms of silver trading and their respective advantages and risks is essential for navigating the silver market effectively.
Physical Silver
Involves purchasing and owning tangible silver bars, coins, or jewellery. Provides ownership and acts as a hedge against inflation. Requires storage and insurance for safeguarding the physical silver.
Spot Silver
Involves buying or selling silver at the current market price for immediate delivery. Provides immediate transactions, enabling quick buying or selling of silver.
Silver Futures
Involves agreeing to buy or sell silver at a predetermined future date for a set price. Provides price stability and a defined contract for future transactions.
Silver ETFs
Allow traders to invest in silver without owning physical silver by tracking the performance of silver prices. Offer diversification within the silver market without direct ownership.
Silver Stocks
Involve investing in shares of silver mining companies, providing indirect exposure to silver by owning shares in silver production companies. Traders can benefit from the performance of silver mining companies’ stocks.
Silver CFDs
Enable traders to speculate on silver price movements without owning the actual silver. Provide leverage, allowing traders to potentially amplify gains, but they carry varying levels of risk due to leverage.

When it comes to venturing into the silver market, having a reliable and regulated broker is paramount. VT Markets offers silver spot and CFD trading with tight spreads, low commissions, and leverage of up to 100:1.
Start trading with VT Markets today by following these three simple steps:
1. Register: Select your preferred account type and submit your application.
2. Fund: Choose from a variety of methods to fund your account.
3. Trade: Select silver in the Precious Metals section or explore more than 1000 instruments across all asset classes.
Additionally, you can test your silver trading strategies with our risk-free demo account. Wishing you the best of luck!
In conclusion, trading silver offers a diverse range of opportunities for both seasoned and novice traders. By understanding the historical significance, dual nature, and trading dynamics of silver, and by following effective trading strategies and risk management, you can successfully navigate the silver market. Consider partnering with reputable brokers like VT Markets to enhance your trading experience and embark on your silver trading journey with confidence and knowledge. Happy trading!