In the shadows of the 17th-century Amsterdam, a groundbreaking financial experiment unfolded, forever altering the course of economic history. The year 1602 saw the birth of the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, a brainchild of the Dutch East India Company, marking the world’s inaugural official stock exchange.

Under the canopy of a buttonwood tree on Wall Street, 24 stockbrokers laid the groundwork for organised securities trading, introducing the novel concept of issuing shares to the public.
Fast forward to today, where the once humble origins have burgeoned into a global financial behemoth. With a staggering size surpassing $100 trillion, the modern stock market stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of those early investors and the evolution of financial markets through centuries.
Whether you’re a novice or a seasoned investor, understanding the basics is key to navigating the complexities of the stock market. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the essentials of stocks and Share CFDs, with a special focus on popular trading strategies.

At its core, a stock symbolises ownership in a company, with popular names like Apple (AAPL), Microsoft (MSFT), Amazon (AMZN), and Google’s Alphabet (GOOGL) exemplifying this ownership’s profound impact. Investors holding these stocks actively participate in globally influential companies.
Beyond theoretical ownership, shareholders hold significant rights. This includes voting on corporate decisions and attending pivotal annual shareholder meetings, allowing active engagement in corporate governance.
Stock ownership’s allure extends to the potential for dividends, a feature prominent in dividend-paying stocks like Johnson & Johnson (JNJ), Coca-Cola (KO), Procter & Gamble (PG), and McDonald’s (MCD). These stocks appeal to investors seeking a steady income stream, enhancing the overall return on investment.
In essence, owning stocks aligns investors with a company’s success and prosperity. It’s not just financial; it’s a connection to brands and businesses shaping our daily lives. Investors in these well-known companies become integral contributors to ongoing success and innovation in the business world.
Major stock exchanges worldwide serve as the epicentres where the world’s most influential stocks are bought and sold, shaping the landscape of global finance. Two giants stand out in this domain – the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ.
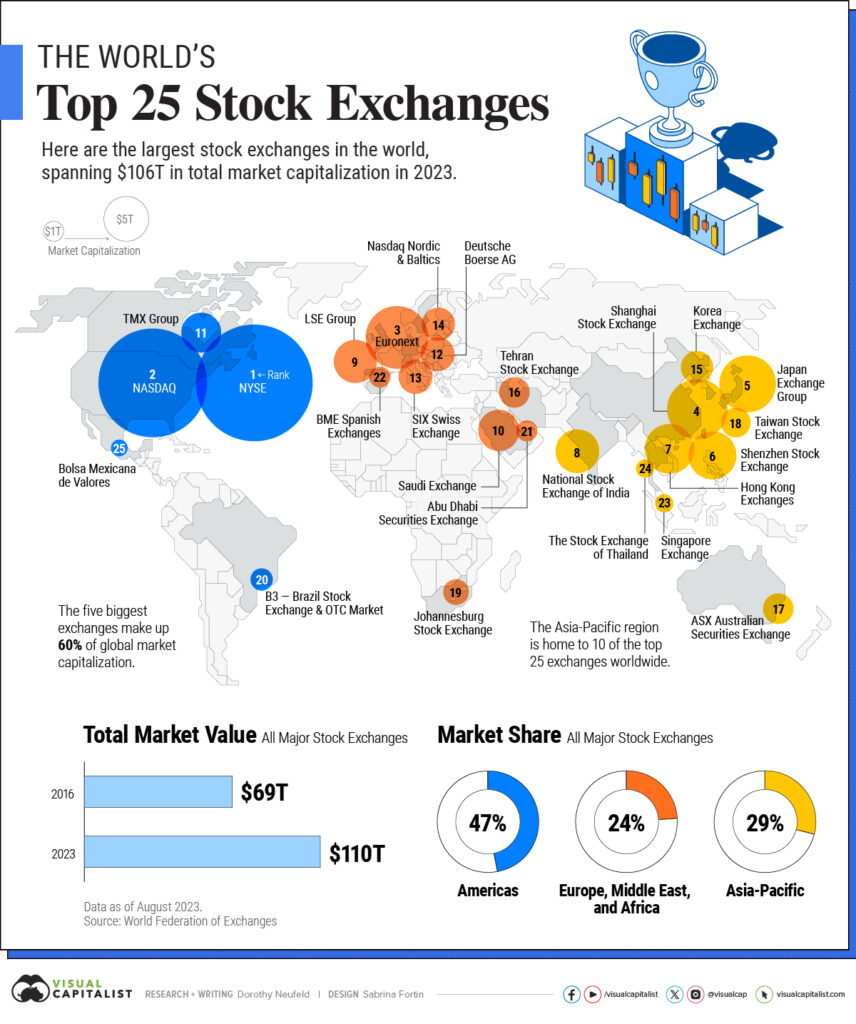
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), located on Wall Street in New York City, is the largest and most prestigious stock exchange globally. It boasts a rich history dating back to 1792, providing a platform for some of the most prominent and established companies.
NASDAQ, on the other hand, is renowned for its technology-focused listings and electronic trading platform. Born in 1971, it has become synonymous with innovation and hosts many of the world’s leading technology companies.
In Europe, the London Stock Exchange (LSE) stands as a financial powerhouse, hosting a diverse array of companies. Meanwhile, the Euronext group, spanning Amsterdam, Brussels, Dublin, Lisbon, Milan, and Paris, plays a pivotal role in European trading.
Turning our attention to Asia, the Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE) in Japan and the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX) command significant influence. These exchanges contribute to the vibrancy and dynamism of the Asian financial markets.
These exchanges are more than mere facilitators; they are the driving forces shaping stock prices globally. The dynamic interplay of supply and demand on these platforms directly influences the valuation of stocks.
Understanding the mechanics of stock exchanges, particularly the NYSE and NASDAQ, is essential for investors seeking to decipher the intricate forces that shape market trends and individual stock prices. As investors, being attuned to the activities on these exchanges equips us to navigate the complexities of the global financial arena.

In the expansive realm of financial instruments, it’s vital to differentiate between various assets. Beyond stocks, investors encounter bonds and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs), each with its unique characteristics.
Bonds, in contrast to stocks, represent debt rather than ownership. When an investor buys a bond, they are essentially lending money to a company or government entity. In return, the bondholder receives periodic interest payments and the eventual return of the principal amount.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs), on the other hand, are investment funds that trade on stock exchanges. ETFs offer a diversified investment approach by bundling together a collection of stocks, bonds, or other assets. They provide investors with a way to gain exposure to a broad market or sector without directly owning individual securities.
Understanding these financial instruments allows investors to tailor their portfolios to match their risk tolerance, investment goals, and preferences.
Share CFDs, or Contracts for Difference, are financial derivatives that allow traders to speculate on the price movements of underlying stocks without actually owning the shares.
Unlike traditional stock trading, where investors physically buy and own shares in a company, CFDs are contracts between traders and brokers.
The derivative nature of CFDs lies in their ability to derive their value from the underlying asset, in this case, stocks. This derivative structure opens up a world of advantages for traders, enabling them to profit from both rising and falling markets.

Advantage 1: Leverage
One of the key advantages of share CFDs is the ability to trade with leverage. Leverage allows traders to control a larger position size with a smaller amount of capital. While this magnifies potential profits, it’s crucial to note that it also amplifies potential losses. This feature makes CFDs an attractive choice for traders seeking to maximise their market exposure without the need for a substantial upfront investment.
Advantage 2: Short Selling
Share CFDs provide a unique opportunity for traders to profit from falling prices through short selling. In traditional stock trading, short selling is often complex and may involve borrowing shares, but with CFDs, this process is streamlined. Traders can take advantage of market downturns by selling CFDs on stocks they anticipate will decline in value, potentially yielding profits even in bearish market conditions.
Advantage 3: Diversification
Diversification is a cornerstone of sound investment strategy, and share CFDs offer a compelling way to achieve it. With CFDs, traders can access multiple assets with a smaller capital requirement compared to traditional stock trading. This not only enhances risk management but also provides the flexibility to explore diverse markets and sectors.
If you’re an active, short-term trader seeking flexibility and leverage, share CFDs are ideal. Designed for day and swing traders comfortable with increased risk, CFDs allow you to profit in both rising and falling markets. With 24/5 trading, global market exposure, and lower transaction costs, they suit those wanting diverse opportunities.
Engaging in share CFDs trading demands a strategic mindset. To streamline your approach, focus on these five essential tips:
1. Thorough Research: Prioritise in-depth research on underlying assets, staying informed about market trends, company performance, and global economic factors.
2. Effective Risk Management: Set clear stop-loss and take-profit levels to manage risks diligently. Discipline in risk management is crucial in the unpredictable world of CFD trading.
3. Understand Leverage: Use leverage judiciously, considering its impact on both profits and potential losses. Avoid excessive leverage to mitigate significant financial risks.
4. Stay Informed: Regularly check economic calendars and major market events. Earnings reports, economic indicators, and geopolitical developments can significantly influence asset prices.
5. Continuous Learning: Embrace ongoing education to stay current on market trends, trading strategies, and industry developments. A commitment to learning enhances trading proficiency and adaptability over time.
Incorporating these key tips into your trading strategy will provide a solid foundation for navigating the dynamic landscape of Share CFDs with confidence.

Discover a wealth of share CFDs trading opportunities with VT Markets, offering access to over 800 leading companies from the US, UK, EU, and Hong Kong.
Leverage up to 20:1 to maximise your trading potential, taking both long and short positions for as low as $0 per trade. This flexibility empowers you to profit from fluctuations in share prices, whether they rise or fall.
Ready to embark on live trading? Open a live trading account with VT Markets for real-time market access. If you’re still refining your strategies, take advantage of the risk-free demo account. Test your approaches and get acquainted with the platform before committing real capital.
VT Markets provides a user-friendly experience for traders of all levels, ensuring you have the tools needed to navigate the dynamic world of share CFDs with confidence.
In conclusion, success in trading stocks and share CFDs demands a strategic approach, disciplined risk management, and continuous learning. Whether you prefer traditional stocks or the flexibility of CFDs, confidence stems from knowledge and a well-crafted strategy. Happy trading!