In the 17th-century Dutch Golden Age, a mesmerising phenomenon called “Tulip Mania” took centre stage, forever changing economic history.
Tulips, normally beloved for their beauty, became the focus of an astonishing speculative bubble. Prices soared to unimaginable heights, with a single rare bulb fetching the value of a grand house in Amsterdam.
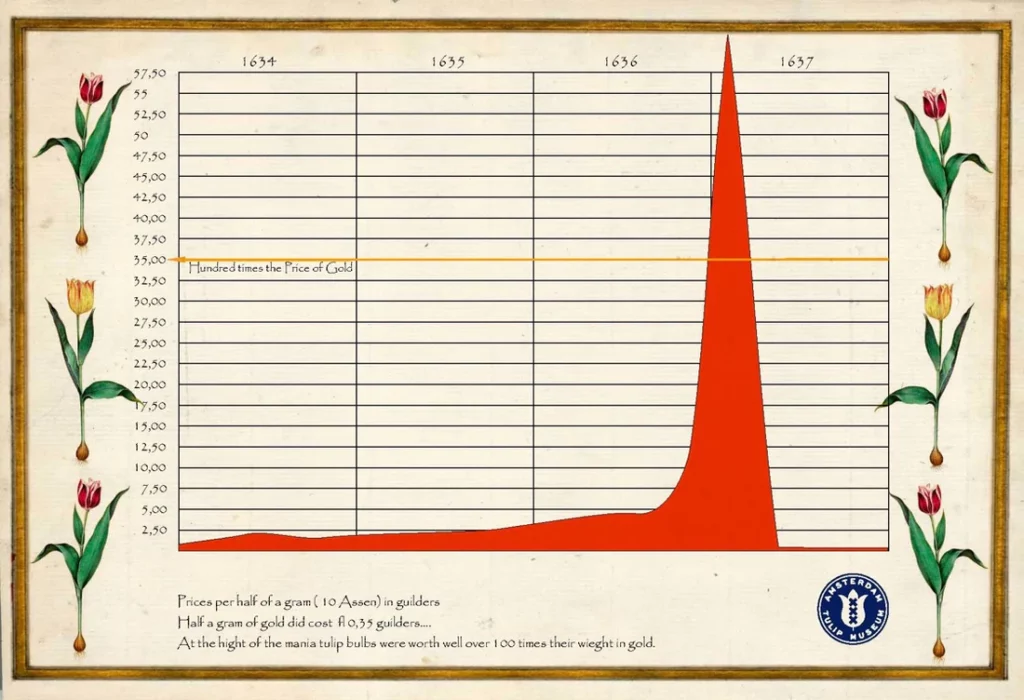
Enthusiastic investors rushed into the tulip trade, lured by the promise of untold riches. However, reality intervened, and the bubble burst, leaving many penniless as prices plummeted.
Tulip Mania remains a powerful lesson in speculative trading and the impact of soft commodities on markets and human behaviour. Soft commodities, the backbone of the global economy and vital for human sustenance throughout history, have a longstanding history of trade spanning centuries.
Today, the soft commodities market has evolved into a highly sophisticated arena, surpassing the archaic bartering systems of the past. Its allure lies in the remarkable liquidity and critical significance of these commodities, presenting traders with abundant opportunities to capitalise on profitable ventures in the global markets.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of soft commodities, elucidating their definition and elucidating the avenues for trading them directly or through financial derivative instruments. Moreover, we will explore the various factors that wield influence over soft commodity prices and delve into effective strategies for managing a diversified portfolio that includes these valuable assets.
Soft commodities refer to natural resources that are cultivated and harnessed for various purposes, including food production, construction, manufacturing consumable goods, and facilitating other human activities.
These products are derived from the earth’s resources but necessitate human effort to be transformed into marketable goods that can be traded. They are commonly referred to as ‘softs’ within the trading industry.
Soft commodities encompass a diverse range of products, originating from various geographical regions worldwide, where optimal conditions favour their production. Despite their distinct origins, these commodities are categorised together due to their indispensable role in human sustenance and their natural composition, which allows for further refining or processing to yield other goods.
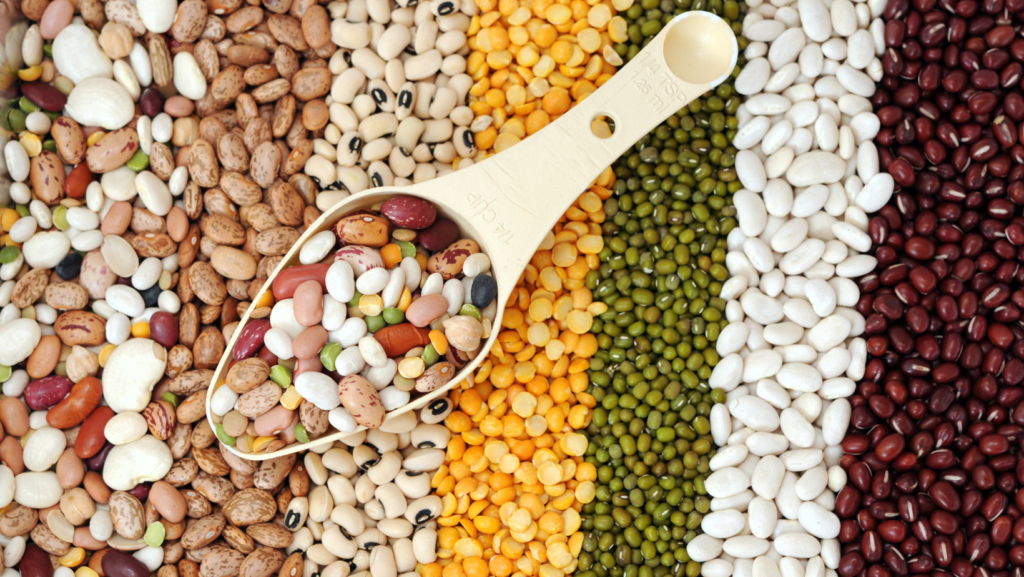

Here are some noteworthy examples of soft commodities:
Coffee beans, Wheat, Cocoa, Sugar, Rough rice, Palm and kernel oil, Cotton, Hogs, Soybeans, Live cattle, Oats, Corn, Lumber.
Given the global nature of their sourcing, soft commodities are subject to price fluctuations influenced by factors such as weather conditions, disruptions in supply chains, and economic uncertainties. These fluctuations create ample opportunities for traders to speculate on the short and long-term movements of their prices.
To grasp the concept of commodities comprehensively, it is essential to distinguish between hard and soft commodities.
Unlike soft commodities that require cultivation and human intervention, hard commodities are directly extracted or mined from the earth and used in their raw, unprocessed state.
These commodities consist of finite natural resources, including crude oil, natural gas, as well as renewable energies such as solar, hydro, wind, and geothermal power.
The price of soft commodities is subject to the influence of various natural and human-related elements. Some key factors include:

The soft commodity market presents compelling opportunities for traders worldwide due to the indispensable nature of these commodities in meeting human needs. The market’s inherent unpredictability and vulnerability to various forces offer both heightened risks and substantial rewards.
While not every trader seeks to embrace such risks, those who thrive on navigating volatile markets can capitalise on lucrative prospects through soft commodity trading.
In today’s sophisticated trading landscape, much of the soft commodities trade occurs through futures markets rather than immediate spot transactions. Futures entail binding contracts that establish fixed prices for soft commodities to be executed on a future date, mutually agreed upon by the buyer and seller.
Initially devised to aid farmers and the agricultural industry in securing favourable prices during off-peak periods, futures have evolved into an integral part of a complex trading ecosystem.
Although futures contracts involve eventual asset delivery, many traders opt to offset futures before the delivery date, leveraging the instrument to speculate on anticipated price movements rather than the intrinsic value of the underlying asset itself. This strategic approach enables traders to engage in dynamic and forward-looking soft commodity trading practices.

Soft commodity trading via futures involves significant risk and requires careful consideration of leverage. Futures contracts enable traders to invest only a percentage of the asset’s full value, yet profits and losses are calculated based on the total price.
Successful predictions can yield magnified profits when offsetting soft commodity futures. However, sudden unpredictable factors may cause price fluctuations, potentially leading to losses surpassing the initial investment.
To mitigate risk, implementing robust risk management strategies is paramount before commencing soft commodity trading. Utilising tools like stop-loss orders can automatically close positions once they reach an unaffordable level, safeguarding against excessive losses.
Additionally, deciding whether to go long or short while trading soft commodities is crucial in formulating an effective strategy.
To gain practical experience, traders can begin with a demo account before transitioning to real trading with a live trading account. VT Markets simplifies this process by providing access to over a thousand financial instruments within an institutional-grade environment.
It’s important to recognise that each soft commodity possesses unique characteristics, including production methods, supply sources, vulnerabilities, and consumer behaviour. For those interested in specific commodities like coffee, comprehensive guides focusing on these particular markets are available to enhance understanding and proficiency.
In conclusion, soft commodity trading offers a rich history and exciting opportunities. From the historic “Tulip Mania” to today’s sophisticated futures markets, these commodities have a significant impact on global economies.
Traders must navigate risks and employ strategies for successful trading. With diverse soft commodities and their unique market influences, there are abundant chances to capitalise on global dynamics. Embrace the allure of soft commodities, learn from history, and explore the complexities of modern trading. Join this exciting journey and seize remarkable opportunities.